Kildibaeva S.R., Kharisov E.I., Suyargulova E.E.
Characteristic modes of hydrocarbon leakage during deep-water accidents. Multiphase Systems. 19 (2024) 4. 137–141 (in Russian).
Characteristic modes of hydrocarbon leakage during deep-water accidents
S.R. Kildibaeva, E.I. Kharisov, E.E. Suyargulova
Sterlitamak branch of Ufa University of Science and Technology, Sterlitamak, Russia
Abstract
Investigation of oil leaks that occur during emergency deep-water hydrocarbon outflows from a damaged well in cases of deposit development
on the World Ocean shelf is of great importance for the safe production of hydrocarbons. To reduce the time required to eliminate those
types of spills it is important to understand the hydrocarbon dispersion dynamics: trajectory, contents, temperature, velocity, etc. Article
considers hydrocarbon flow (oil, gas, hydrate) for cases of their deep-water outflow from a damaged well, main thermophysical dependencies,
typical stage transition coordinates, and coordinate change dynamics of transition of jet to plume depending on the initial conditions
was analysed. Integral Lagrangian method of control volume was used for calculations.
Keywordshydrocarbons,
submerged jets
Article outline
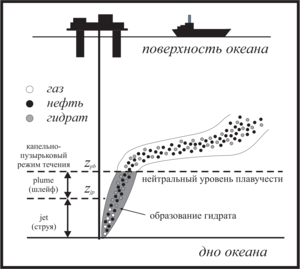
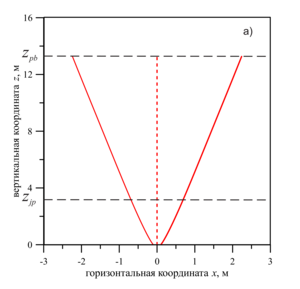
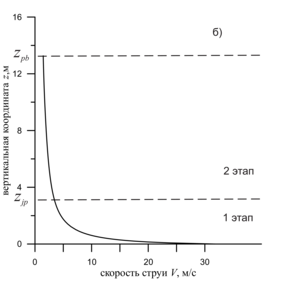
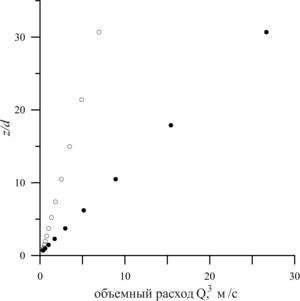
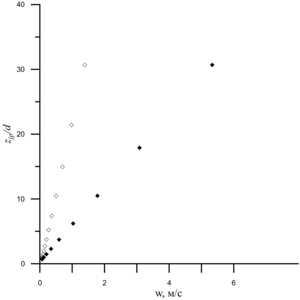
The development of deep-sea oil deposits in the World Ocean is attractive due to the practically untouched reserves of extracted hydrocarbons. The danger of such mining is associated with a high probability of contamination of the water area in the event of a man-made leak. The study of oil leaks that occur during emergency deep-sea spills in cases of field development in the shelf of the World Ocean is of great importance for the safe production of hydrocarbons. To reduce the time to eliminate such leaks, it is important to understand the dynamics of hydrocarbon propagation: their trajectory, composition, temperature, speed, etc. One of the key features of hydrocarbon migration at great depths and high pressures is the process of formation of hydrate shells on the surface of associated gas bubbles. Hydrate formation can affect the dynamics of hydrocarbon migration, as well as complicate the process of eliminating leakage, as was the case with the oil spill in the Gulf of Mexico. To eliminate the spill, an attempt was made to install a dome, but gas hydrates, accumulating inside the dome, gave it undesirable buoyancy and did not allow the device to be fixed. The migration of hydrocarbons occurs in several stages: a turbulent jet (jet), a plume (plume) and a drip-bubble mode. The purpose of this work is to study the process of transition of the jet stage of the flow into the plume. According to the problem statement, the flow of hydrocarbons is determined by the following initial conditions: the radius of the outflow source r, the volume flow rate of incoming hydrocarbons (oil and gas), the thermophysical characteristics of the environment and the characteristics of hydrocarbons coming from the source. We believe that the environmental conditions correspond to the conditions of stable hydrate existence, therefore we take into account the process of hydrate formation on the surface of bubbles. To describe the migration of hydrocarbons, a closed system of equations is used, including equations of conservation of mass, momentum and energy, as well as a number of auxiliary equations. The modified integral Lagrangian control volume method (ILMCO) was used for calculations. According to this method, the jet is considered as a sequence of elementary cylindrical volumes, each of which is characterized by a position in space, linear dimensions, averaged values of the composition of hydrocarbons, temperature, velocity, etc. In order to determine the effect of the mass content of the jet stream components on the dynamics of hydrocarbon migration and the transition of the jet stream to the plume, a series of computational experiments was conducted. In the first case, the initial volume flow rate of the gas was changed. Each time, the initial volume consumption of gas increased by 20%. In the second case, the initial volume consumption of oil changed similarly. According to the analysis, the dependence of zjp/d on Q is linear, however, in the case when the volume flow rate of the gas changed, the coordinate of the section grows more intensively. This is due to the higher rate of hydrocarbon migration. The paper considers the stages of the flow of hydrocarbons (oil, gas, hydrate) that occur during deep-sea emergency spills: turbulent jet, plume, drip-bubble regime. The trajectory of the hydrocarbon flow for the case of no flow and the dependence of the hydrocarbon migration rate on the vertical coordinate for flow stages 1-2 are obtained. The dynamics of the change in the coordinate of the transition of the jet stream to the plume flow, depending on the initial conditions and the composition of the flow, is analyzed.
References
- Бондарев Э.А., Рожин И.И., Аргунова К.К. Обобщенная математическая модель образования гидратов в магистральных газопроводах //
Прикладная механика и техническая физика. 2019. Т. 60, № 3(355). С. 120–127.
DOI: 10.15372/PMTF20190312
Bondarev E.A., Rozhin I.I., Argunova K.K. Generalised Mathematical Model of Hydrate Formation in Main Gas Pipelines // Applied Mechanics and
Technical Physics. 2019. Vol. 60 (3). Pp. 503–509.
DOI: 10.1134/S002189441903012X
- Рожин И.И., Иванов Г.И. Моделирование образования гидратных пробок при совместной работе газоносного пласта и скважины для случая
зависимости равновесных условий гидратообразования от состава пластовых вод // Прикладная механика и техническая физика. 2023. Т. 64,
№ 2(378). С. 127–142.
Rozhin I.I.I., Ivanov G.I. Modelling of hydrate plug formation during joint operation of gas-bearing reservoir and well for the case of dependence
of equilibrium conditions of hydrate formation on the composition of formation water // Applied Mechanics and Technical Physics. 2023. V. 64,
No. 2(378). Pp. 127–142 (In Russian).
DOI: 10.15372/PMTF202215120
- Мусакаев Н.Г., Уразов Р.Р., Шагапов В.Ш. Динамика образования гидратов при транспортировке природного газа // Теплофизика и аэромеханика.
2006. Т. 13, № 2. С. 295–302.
EDN: hvuvkp
Musakaev N.G., Urazov R.R., Shagapov V.Sh. Hydrate formation kinetics in piped natural-gas flows // Thermophysics and Aeromechanics. 2006. Vol. 13,
No. 2. Pp. 275–281.
DOI: 10.1134/S0869864306020090
- Уразов Р.Р., Чиглинцев И.А., Насыров А.А. Образование склеротических отложений гидрата в трубе для отбора газа из купола-сепаратора //
Инженерно-физический журнал. 2017. Т. 90, № 5. С. 1223–1231.
DOI: znlkyv
Urazov R.R., Chiglintsev I.A., Nasyrov A.A. Formation of Sclerotic Hydrate Deposits in a Pipe for Extraction of a Gas from a Dome Separator // Journal
of Engineering Physics and Thermophysics. 2017. Vol. 90, No. 5. Pp. 1162–1169.
DOI: 10.1007/s10891-017-1670-2
- Chiglintsev I.A., Nasyrov A.A. Modeling of the process of filling a dome separator with the decomposition of a gas hydrate formed during the mounting
of the installation // Journal of Engineering Physics and Thermophysics. 2016. V. 89, No. 4. Pp. 854–863.
DOI: 10.1007/s10891-016-1446-0
- Sammarco P.W., Kolian S.R., Warby R.A.F., Bouldin J.L., Subra W.A., Porter S.A., Distribution and concentrations of petroleum hydrocarbons associated
with the BP/Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill, Gulf of Mexico // Marine Pollution Bulletin. 2013. V. 73, No. 1. Pp. 129–143.
DOI: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2013.05.029
- Кильдибаева С.Р., Столповский М.В. Этапы накопления капель нефти и пузырьков газа в куполе для случаев глубоководных разливов: часть 1 //
Электронный научный журнал Нефтегазовое дело. 2023. № 6. С. 57–75.
Kildibaeva S.R., Stolpovsky M.V. Stages of Accumulation of Oil Droplets and Gas Bubbles in the Dome for Cases of Deep-Sea Spills: Part 1 // Oil and
Gas Business. 2023. No. 6. Pp. 57–75. (in Russian)
DOI: 10.17122/ogbus-2023-6-57-75
- Кильдибаева С.Р., Гималтдинов И.К. Динамика многофазной затопленной струи с учетом образования гидратов // Вестник Тюменского
государственного университета. Физико-математическое моделирование. Нефть, газ, энергетика. 2015. Т. 1, № 3. С. 92–101.
Kildibaeva S.R., Himaltdinov I.K. Dynamics of multiphase flooded jet with consideration of hydrate formation // Bulletin of Tyumen State University.
Physico-mathematical modelling. Oil, gas, energy. 2015. Vol. 1, No. 3. Pp. 92–101 (In Russian).
EDN: vvrhnz
- Kildibaeva S.R., Gimaltdinov I.K., Kharisov E.I. Conduction of a Laboratory Experiment with the Goal of Researching Submerged Flow Peculiarities //
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science. 2022. V. 988. Pp. 042049.
DOI: 10.1088/1755-1315/988/4/042049
- Кильдибаева С.Р., Харисов Э.И. Трехмерная визуализация модели течения многофазной затопленной струи // Вестник Южно-Уральского
государственного университета. Серия: Математическое моделирование и программирование. 2023. Т. 16, № 1. С. 69–80.
Kildibaeva S.R., Kharisov E.I. Three-Dimensional visualization of the submerged jet flow model // Bulletin of the South Ural State University, Series:
Mathematical Modelling, Programming and Computer Software. 2023. Vol. 16. No. 1. Pp. 69–80. (in Russian)
DOI: 10.14529/mmp230106
- Daskiran C., Cui F., Boufadel M.C., Zhao L., Socolofsky S.A., Ozgokmen T. Hydrodynamics and dilution of an oil jet in crossflow: The role of small-scale
motions from laboratory experiment and large eddy simulations // International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow. 2020. V. 85. P. 108634.
DOI: 10.1016/j.ijheatfluidflow.2020.108634
- Lee J.H.W., Chu V.H. Turbulent jets and plumes — a Lagrangian approach. Kluwer, 2003. 390 p.
- Yapa P.D., Dasanayaka L.K., Bandara U.C., Nakata K. A model to simulate the transport and fate of gas and hydrates released in deepwater // Journal
of Hydraulic Research. 2010. V. 48(5). Pp. 559-572.
DOI: 10.1080/00221686.2010.507010
- Zheng L., Yapa P.D., Chen F. A model for simulating deepwater oil and gas blowouts – part I: theory and model formulation // Journal of Hydraulic
Research. 2002. V. 41, No. 4. Pp. 339–351.
DOI: 10.1080/00221680309499980
- Yapa P.D., Li Z. Simulation of oil spills from underwater accidents I: Model development // Journal of Hydraulic Research. 1997. V. 5(5). Pp. 673–688.
DOI: 10.1080/00221689709498401
- Chen F., Yapa P.D. Modeling gas separation from a bent deepwater oil and gas jet/plume // Journal of Marine Systems. 2004. No. 45. Pp. 189–203.
DOI: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2003.11.005