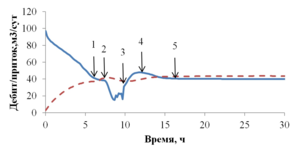
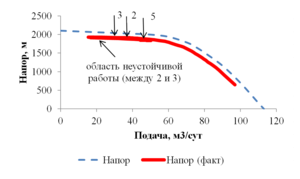
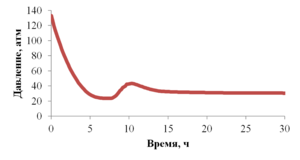
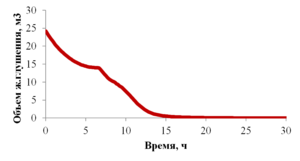
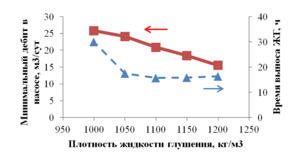
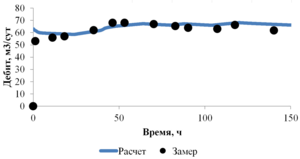
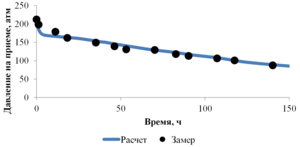
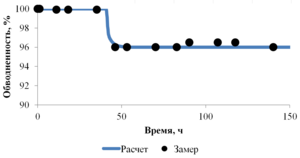
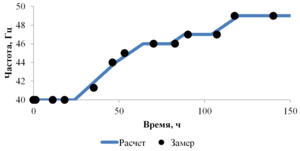
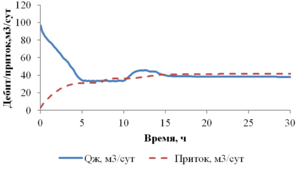
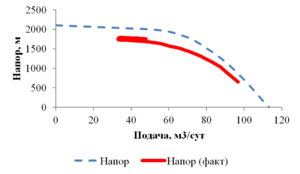
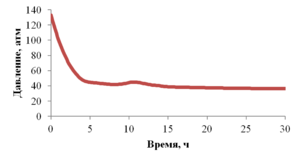
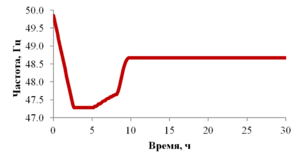
The paper presents the results of mathematical modeling of the process of launching and output to the mode of an oil well, which was uploaded by a well-killing liquid at the stage of repairs. After the launching of the electric submergible pump the drop of the bottomhole pressure occurs and the inflow of reservoir fluid begins. As a result the multicomponent mixture is generated inside the well, which consists of oil, associated water, well-killing liquid and free gas, originated from the oil during degassing, and this mixture is pumped out towards wellhead. As soon as the pump characteristics are changed, when the liquid with variable density is pumped out, it is necessary to control the speed of a shaft of the pump for providing the stable pump regime. This problem is solved in the paper for different ratios of densities of well-killing liquid and reservoir fluid by the mathematical modeling of multiphase flow in the well elements and inside the pump. As a mathematical model the one-dimensional quasi-stationary model in approach of drift for description of relative motion of the components is applied, which proved itself well for modeling of non-stationary processes lasting for several days. The comparison of calculated and measuring field parameters is presented. It is shown that the speed of washout of the well-killing liquid from the oil well and the probability of the pump stop due to its head failure depend on the ration of densities of the well-killing liquid and reservoir fluid. It is stated that the monitoring of change of parameters of the pump in time through the mathematical modeling can help to optimize the output to the mode of the well. This allows to avoid stops due to the pump head failure and to diminish the electricity costs.
multiphase flow,
non-stationary flow,
oil well
Purpose:
Monitoring and optimization of periodical regime of oil wells, which are operated by sets of electrical submersible pump, by the help of mathematical modeling methods
Methodology:
To describe the flow in the reservoir and well 1D single-phase and two-phase non-stationary models are used. In the case of description of flow inside the well the model accounts for difference between the velocities of gas and liquid, mass transfer associated with gas extraction from the oil and the character of the flow (laminar-turbulent, bubble-slug). The mathematical model allows to provide calculations with fixed durations of working and accumulation cycles, and is used for solving the inverse problem, if it is necessary to optimize the regime of operation of the well in terms of getting the maximum possible oil rate.
Findings:
The model problem for the cylindrical tube is solved, which enables to estimate the typical time duration of the processes occurring in the well. By examples of calculation of periodical regime of wells in the field conditions it is shown that the model appropriately describes the physical processes. The results of optimization are presented, which demonstrate the possibility to gain essential increase of oil at the wells.
Conclusions:
1) Due to extended size of well and multiphase effects associated with heat and mass transfer the setup of stationary regime of the flow occurs only after several hours since the boundary conditions changes. With reference to the wells, which are operated in the regime of periodical starts and stops of a pump, this means that the multiphase flux in wells is always non-stationary.
2) In terms of description of non-stationary processes in the well a mathematical modeling is a good instrument for monitoring of the actual regime of well operating and its optimization. In the absence of filed measurements of operating parameters the modeling allows to get it by simulation.