The problem of ice formation in a dry, cold, porous medium saturated with ice and gas (air) when pumping warm water
is considered in a flat one-dimensional self-similar formulation. The task was considered in volume area. During the
injection of warm water from the beginning deep into the reservoir, it spread in a volume region that will divide the
reservoir into 3 zones. The first zone was filled with water, the second zone was filled with ice and water, and the third
zone was filled with ice and gas. To describe the process of heat and mass transfer, the following hypotheses were
used: the temperature of the saturated substance (water, ice or gas) is equal to the temperature of the porous medium;
ice and skeleton still; water, ice and skeleton of the reservoir are incompressible; skeletal porosity is constant. On the
basis of constructed self-similar solutions, a numerical analysis was performed illustrating the effect of the initial
parameters of a dry porous medium saturated with ice and gas, as well as the temperature of the injected water on
the temperature and pressure distribution in the porous medium. It has been established that an increase in the
temperature of the injected water does not lead to a significant increase in the area of ice decomposition. It is also
established that if the pressure of the injected water is increased, this will not lead to a large increase in the area of
ice decomposition. However, based on the results obtained, it can be seen that the speed of movement of the melting
boundary increases, in particular, as the pressure increases by
phase transition,
ice melting,
water-ice,
ice melting modeling,
porous medium,
phase transition
The purpose of this scientific article is to build a theoretical mathematical model of the process of melting ice during the injection of warm water into a porous medium.
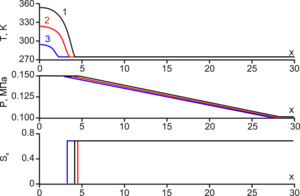
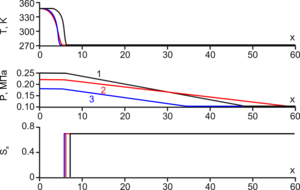
The problem deals with a flat one-dimensional self-similar formulation for a porous medium, which is divided into three zones: the first zone, which is filled only with water, the second zone, is filled with ice and water,
and in the third zone, the pores are filled with ice and gas. The solution is found by introducing a self-similar variable
Solution Method: Solving the system of equations obtained in the course of the study numerically, for example, using the iteration method, we obtained results that can be applied in practice.
Results: For the task, solution algorithms were found, and corresponding graphs for pressure, temperature, and ice saturation were constructed. It was found that it is economically more profitable
to pump water with a lower temperature because water with a higher temperature slightly increases the freezing area of the porous soil. Still, if you increase the pressure on